NIT released its latest shortwave infrared (SWIR) imaging technology
Recently, NIT (New Imaging Technologies) released its latest shortwave infrared (SWIR) imaging technology: a high-resolution SWIR InGaAs sensor, specifically designed to meet the most demanding challenges in this field.
The new SWIR InGaAs sensor NSC2101 boasts remarkable features, including an 8 μm sensor pixel pitch and an impressive 2-megapixel (1920 x 1080) resolution. Even in challenging environments, its ultra-low noise of just 25 e- ensures exceptional image clarity. Additionally, the dynamic range of this SWIR sensor is 64 dB, enabling precise capture of a wide spectrum of light intensity.
- Spectral range from 0.9 µm to 1.7 µm
- 2-megapixel resolution – 1920 x 1080 px @ 8μm pixel pitch
- 25 e- readout noise
- 64 dB dynamic range
Designed and manufactured in France by NIT, the high-performance SWIR InGaAs sensor NSC2101 offers unparalleled performance and reliability. Leveraging advanced technology and expertise, NIT has meticulously crafted a sensor that meets the stringent standards of ISR applications, providing crucial insights and intelligence across various scenarios.
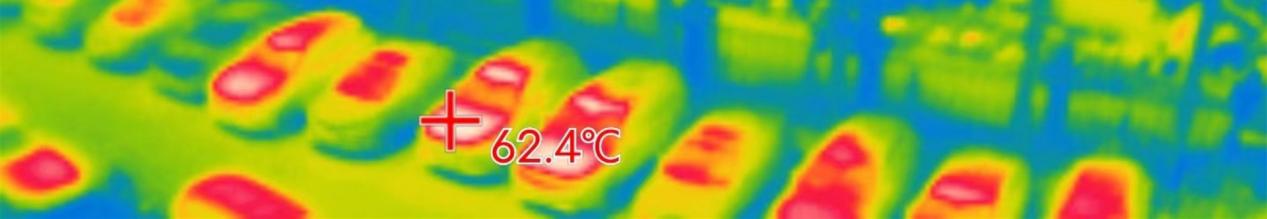
Photos taken with the SWIR sensor NSC2101
The SWIR sensor NSC2101 has a wide range of applications, suitable for industries such as defense, security, and surveillance. The sensor’s capabilities are vital for enhancing situational awareness and decision-making, from monitoring border security to providing critical intelligence in tactical operations.
Furthermore, NIT’s commitment to innovation extends beyond the sensor itself. A thermal camera version integrating the SWIR sensor NSC2101 will be released this summer.
The development of the NSC2101 is part of a broader trend in the evolution of thermal imaging technologies. Traditionally, thermal imaging has relied on longwave infrared (LWIR) sensors to detect heat emitted by objects, providing critical insights in low-visibility conditions. While LWIR sensors excel in many scenarios, the advent of SWIR technology marks a significant advancement in thermal imaging.
SWIR sensors, such as the NSC2101, detect reflected light rather than emitted heat, enabling imaging through conditions where traditional thermal sensors might struggle, such as through smoke, fog, and glass. This makes SWIR technology a valuable complement to LWIR in comprehensive thermal imaging solutions.
Advantages of SWIR Technology
SWIR technology bridges the gap between visible light and thermal imaging, offering unique advantages:
- **Improved Penetration**: SWIR can penetrate through smoke, fog, and even certain fabrics, providing clearer images in adverse conditions.
- **High Resolution and Sensitivity**: The NSC2101’s high resolution and low noise levels ensure sharp, detailed images, which are crucial for applications requiring precise visual information.
- **Broad Spectrum Imaging**: With its spectral range of 0.9 µm to 1.7 µm, the NSC2101 captures a wider range of light intensities, enhancing the detection and analysis capabilities.
Applications in Modern Industries
The integration of SWIR sensors in thermal imaging is transforming various sectors. In defense and security, SWIR enhances surveillance capabilities, enabling better monitoring and identification of threats. In industrial applications, SWIR aids in material inspection and process monitoring, detecting defects and irregularities that are invisible to the naked eye.
Future Prospects
NIT’s introduction of the NSC2101 signifies a step forward in the convergence of imaging technologies. By combining the strengths of SWIR and traditional thermal imaging, NIT is paving the way for more versatile and robust imaging solutions. The upcoming camera version of the NSC2101 will further expand its applicability, making advanced imaging technology accessible for a broader range of uses.
Post time: Jun-07-2024